You could say lead-gen leaders understand hedging.
Showing posts with label video marketing. Show all posts
Showing posts with label video marketing. Show all posts
Friday, January 5, 2018
Hedging
Tuesday, March 28, 2017
Government Communicators: Know Who's Who in a Video Crew
 |
| Photo: Patty Mooney |
You probably deal with video crews often in your role as a government communicator. You host press conferences and other events broadcasters want to cover.
From the broadcaster's point of view, any shooting done is considered "field" or "remote" shooting; and it will send specialized crews for it. However, you may not be clear about the taxonomy and makeup of these crews.
Why do some field crews seem to waltz into any situation on their own, shoot it, and pack out with hardly a word, while others can't be satisfied without detailed advance support and extra time, space, access, and control on site?
The answer lies in the differences between two types of field crews: ENG versus EFP.
The two types of crews have considerably different purposes and needs. Understanding the differences can reduce your headaches and improve your media coverage.
ENG–Electronic News Gathering
ENG refers to a field news team covering a current or breaking story. The term derives from TV news in the 1980s, when field footage was first electronically transmitted to editors, instead of being handed off to them on videotapes.
 |
| Photo: Alex Row |
For high-profile or unfolding situations, a satellite uplink or a microwave truck might also be dispatched to the location for live transmitting, and to serve as home-base for multiple ENG crews. Regardless of size, ENG crews are used by TV, web and radio broadcasters to cover press conferences, crime scenes, public events, accidents, rescues, storms, court trials, and battle zones. ENG crews are “on call” day and night for immediate deployment to "get the story." Some stories–a hostage situation, a major fire, or a riot, for example–may attract dozens of crews, who vie for position as the event unfolds.
For an ENG crew, the emphasis is on speed, agility, and fast turnaround of short-form stories, usually for airing the same or the following day. Their set-up and tear-down process is fast; they need minimal B-roll footage (“covering shots"); and, since they are reporting at public press events, don’t need to get appearance releases signed. You will hear them use the term “run-and-gun,” which is the signature ENG style.
As a communications professional in charge of a government event such as a press conference, you and your team will need to accommodate each broadcaster’s ENG crew: give them the event rundown, and let them know how to get into the venue. When crews arrive, show them to the area where they can set up; and let them know if there will be press availability time with the VIP for individual questions. Crews will usually have batteries, but show them a power source for backup. Tell them if they will need to acquire audio using their own mics; otherwise help each crew plug into to your "mult box" for a direct audio feed from the podium or soundboard. (A mult box is a single audio source with multiple outputs. Mult boxes are commonly used at press conferences in small spaces, so that umpteen mics are not all in the speaker’s face at the same time, and so that reporters can all get the same, clean audio.) Crews will want a couple of minutes to run a sound check before the event starts and cameras begin to roll. If your event is happening someplace with local color or visual interest, you should also arrange a few minutes for the cameras to shoot some B roll. After the event, ask the crews if there’s anything else they need, and show them the best way out.
EFP–Electronic Field Production
The EFP crew works to create a narrative, rather than reacting to an unfolding story in real time. Whereas short-form news packages or live stories are the norm for local reporters, longer-form, in-depth stories are covered by national news magazines. In addition, you may want your agency’s in-house video production team (or a crew that you hire) to make a video out of an event as an edited package, or to create "Bites and B roll" to be made available to broadcasters for their use. Any of these more complex situations will call for an EFP crew.
According to the Herbert Zettl's Television Production Handbook:
"[Electronic Field Production] uses both ENG and studio techniques. From ENG it borrows its mobility and flexibility; from the studio it borrows its production care and quality control. EFP takes place on location (which may include shooting in someone’s living room) and has to adapt to the location conditions… Good lighting and audio are always difficult to achieve in EFP, regardless of whether you are outdoors or indoors. Compared to ENG, in which you simply respond to a situation, EFP needs careful planning.”
Typical uses of EFP are: industrial videos (i.e., non-broadcast, which includes government videos), documentary, broadcast magazine interviews and profiles, and promos.
 |
| Photo: Ann Ramsey |
 |
| Photo: Ann Ramsey |
EFP usually has higher production values and slower turnaround than ENG. As the government communicator, you want to assist the EFP crew to make a terrific video, one that's assured of getting aired. Help them with: scouting locations, securing interviews, and accessing the venue. For unloading, look for alternatives to stairs (since they usually put all their equipment on a rolling cart, EFP crews need elevators or ramps). For set-up, give them space to stage equipment, and allot them at least an hour to light the interview set. EPF crews will want attractive interviews, so they need extra room (“throw”) behind the interviewee to blur out the background. They also need to minimize disturbances and light and sound interference once the cameras are rolling. For multiple interviews, you might want to arrange a separate room that can be pre-lit. You should also accompany the crew to B-roll locations, to ensure they get access and can get the variety of shots they need. Don't be surprised if a two- or five-minute finished piece requires a day or more of production time. At the end of the shoot, ensure the crew was able to get signed appearance and location releases, and give them adequate time to pack up and load out.
Different animals
Because ENG and EFP crews are different animals, they demand different care and feeding. To complicate matters, it's possible you'll find both types of crews covering a single event. So you need to:
- Understand that ENG crews, although more self-sufficient, are concerned about their deadlines. So if they request something, they need it on the double! As appropriate, you will be directing your ENG crews to one or more designated press areas from which they can cover the main podium, plus any immediate follow-ons, such as press avails or facility tours.
- Understand, in contrast, that EFP crews will likely need pre-arranged, one-on-one interviews and multiple set-ups, so they'll require additional space, time and attention during, as well as after, the formal event. Don't begrudge them the time and trouble. The compensation for the extra effort you give EFP crews will show up in the end result: a high-quality, in-depth and compelling video.
Normally, these roles are combined varyingly among a small crew:
- Producer/Reporter - directs crew, conducts interviews
- DP (Director of Photography) - chief camera person
- Videographer - camera person, e.g., second camera
- Sound Recordist - acquires and mixes audio
- Boom Operator - sound recordist who uses a pole-mounted mic
- AP (Associate Producer) - assists producer with logistics
- Gaffer - lighting director
- Grip - assist the DP and sets up the camera rigging
- Dolly Grip - operates a camera dolly
- PA (Production Assistant) - manages gear
- Media Manager - relays or transfers video and audio files
Monday, January 16, 2017
Where Should CMOs Invest in 2017?
Video. Video drives brand engagement and can boost conversion rates on landing pages by 80%.
Digital. "Customers in 2017 will be digital; be there," said Craig Cooke, CEO of Rhythm.
Employee engagement. Invest inside, and turn every employee into a sales evangelist.
Social. Social is the most organic way to market your business. But it takes work, so hire someone outside to do it.
Website. A content-rich website improves SEO, boosts traffic, and keeps audiences on your site, rather than some network.
PR. "The art of great storytelling through media isn’t going away," said Nicole Rodrigues, CEO, NRPR Group.
Content. "Content shock" makes quality content today's key differentiator.
To a man with a hammer, everything looks like a nail. Forbes polled only traditional and digital agencies, omitting the experiential. So, I'll add:
Events. Done well, nothing―absolutely nothing―accelerates brands faster. My humble opinion? Move events to the top of your list.
Tuesday, August 9, 2016
Where's the Thought in Thought Leadership?
While the stuff served daily through most B2B marketers' Tweets, videos, blog posts and e-books looks tasty and can be consumed quickly, it isn't particularly satisfying. Or good for you.
Although there are thousands of exceptions, most B2B marketers rush out junk, contributing to the deafening "content shock" Mark Schaefer describes.
Plainly, simply, thought leadership shouldn't be advertising. It's supposed to be content that's authentic and that articulates leading-edge thinking, not your marketing department's social media strategy.
And thought leadership shouldn't be about media. It's supposed to focus on thought, not LinkedIn or Meerkat or Snapchat.
B2B marketers are hacking the system when they publish non-nutritional content, however carefully it's dressed to resemble food for thought.
And thought leadership shouldn't be about media. It's supposed to focus on thought, not LinkedIn or Meerkat or Snapchat.
B2B marketers are hacking the system when they publish non-nutritional content, however carefully it's dressed to resemble food for thought.
Ironically, every B2B marketer could contribute thought leadership, if only she trusted the few thoughtful individuals inside her organization—and they trusted themselves. Sadly, neither do.
"Thought leaders focus on crafting ideas, not audience reaction and reach," says digital marketer Walter Adamson in Firebrand.
He's 100% right. Thought leaders don't lean on vapid videos and tricked up infographics to entreat customers. They rely instead, TEDishly, on "ideas worth sharing."
"Being a thought leader means putting your own personal thoughts out there in whatever form appeals to you," Adamson says. "It’s not about the medium. It’s about the message and it’s about filling in the white spaces which teams of content producers don’t even know exist."
He's 100% right. Thought leaders don't lean on vapid videos and tricked up infographics to entreat customers. They rely instead, TEDishly, on "ideas worth sharing."
"Being a thought leader means putting your own personal thoughts out there in whatever form appeals to you," Adamson says. "It’s not about the medium. It’s about the message and it’s about filling in the white spaces which teams of content producers don’t even know exist."
Thursday, July 28, 2016
A Nation of Videots
A Facebook exec recently predicted her platform would be "all video" in five years.
Her prediction should neither surprise nor disturb you in the least bit.
The social platforms like Facebook are becoming gargantuan public access TV stations. Think Wayne's World meets Warhol's World. Everyone will be famous for 15 minutes, because every schmo will have a show.
Face the fact: we are a nation of videots.
It's why we retweet videos more than text messages; why the appearance of the word “video” in an email's subject line boosts opens; why YouTube is the second most-used search engine; and why Facebook is going "all video."
Mindset, not media, determines what's expressed, as Aldous Huxley said 80 years ago. We like only what we can like; what we're psychologically capable of liking; what we're conditioned to like.
"The Zeitgeist is just professor Pavlov on a cosmic scale."
We like video.
That's why every marketer had better climb on the video bandwagon. And if you're not convinced, chew on these findings from Animato:
We like video.
That's why every marketer had better climb on the video bandwagon. And if you're not convinced, chew on these findings from Animato:
- 96% of customers find videos help purchase decisions
- 77% think companies that market with videos are more engaging
- 71% say those videos give them a positive impression of the company
- 58% consider companies that market with videos are more trustworthy
Monday, May 30, 2016
How to Inveigle More Visitors with Video
Video is every storyteller's super weapon.
In no other industry does this hold truer than in travel.
In no other industry does this hold truer than in travel.
By immersing viewers in sights and sounds—people, places, foods and comforts—video grabs the emotions and sparks the imagination.
Well-made and placed videos, in fact, speed would-be visitors from consideration to booking, according to Expedia.
But what makes a video effective?
But what makes a video effective?
The video must cut through the clutter. To be noticed in a crowded space, your video must focus on epic—and iconic—experiences.
The video must be first person. The more immersive, the more inspiring. Storytelling that's first person produces a "you are here" effect.
The video must be integrated. Breathtaking content only gets you so far. Bookings result from strategic messaging, placement and integration.
Expedia points to Visit Denmark as producers of effective videos.
The DMO's award-winning productions not only tell intriguing first-person stories, but encourage viewers to learn more about destinations like Copenhagen and Aarhus.
Tuesday, May 17, 2016
The Experience Stack
Mobility has fundamentally changed computing, he says.
While desktop computing was all about your timeline-based profile (think Facebook), mobile computing is about in-the-moment self-expression (think Snapchat).
With the onrush of mobility, "You are not a profile. You are simply you."
We've all become, in effect, amateur auteurs.
"The stories we tell each other now begin and end visually, making the narrative more literal than ever," Wadhera says.
Providers are racing to monopolize mobility by building a pile of immersive toys he calls the experience stack (pictured here).
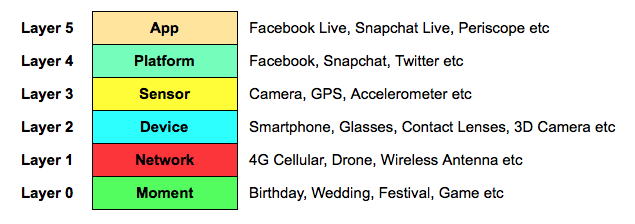
"The full stack is in service of capturing and communicating real-world moments," Wadhera says. "Reality is its foundation. As you move up, the layers transition from physical to logical. At the top is the application layer made up of products like Snapchat Live and Periscope."
Tomorrow’s toys will boggle our storyteller's brains, Wadhera says.
"Our online and offline identities are converging, the stories we tell each other now start and end visually and investments at every layer of a new stack are accelerating the development of experience-driven products. Taken together, these trends have cracked open the door for a new golden age of technology."
Wednesday, April 13, 2016
You Don't Have to be Jewish
Once upon a time, I had the privilege of interviewing madman George Lois for a magazine article about ad creative.
When I asked, "What makes an ad effective?" Lois said, "An ad has to kick you in the ass with an idea you like."
In other words, the advertiser needs to startle you, then evoke a little love.
Last year's most-shared ads, according to Unruly, did just this.
Each ad transmitted a powerful idea by marshaling a string of surprising sounds and images that, taken together, can't help but excite love… at least a little.
As Don Draper said in Mad Men, “Advertising is based on one thing: happiness. And you know what happiness is? Happiness is the smell of a new car. It's freedom from fear. It's a billboard on the side of the road that screams reassurance that whatever you are doing is okay. You are okay.”
And now for last year's most-shared ad…
Read more about emotion's role in advertising here.
When I asked, "What makes an ad effective?" Lois said, "An ad has to kick you in the ass with an idea you like."
In other words, the advertiser needs to startle you, then evoke a little love.
Last year's most-shared ads, according to Unruly, did just this.
Each ad transmitted a powerful idea by marshaling a string of surprising sounds and images that, taken together, can't help but excite love… at least a little.
As Don Draper said in Mad Men, “Advertising is based on one thing: happiness. And you know what happiness is? Happiness is the smell of a new car. It's freedom from fear. It's a billboard on the side of the road that screams reassurance that whatever you are doing is okay. You are okay.”
And now for last year's most-shared ad…
Read more about emotion's role in advertising here.
Sunday, March 20, 2016
The Future of B2B Content Marketing
Videos are the future of B2B content marketing.
Seven in 10 B2B marketers already use them, according to Demand Metric.
That's little wonder, when one in two people watch marketing videos on line every day, as Liz Alton reports in Sales and Marketing Daily Advisor.
Videos' matchless power comes from their "immediacy and intimacy," Alton says.
She describes five kinds of videos B2B marketers use:
Explainer. Explainer videos are "short, focused videos that give an elevator pitch of what products and services you offer." They're often produced in whiteboard style.
Case studies. Case studies give customers "an inside look at your work," Alton says. They can be testimonials or project reviews that prove you deliver results.
How-to. How-to videos address FAQs you receive. Depending on the complexity of the topic, they can provide quick tips or in-depth guidance.
Real-time. Meerkat and Periscope let you connect with customers in the moment. "Companies are using the tools for live Q&As, to report in from events and trade shows, and to respond to industry news," Alton says.
Culture. Culture videos let you showcase staff, illustrate workflows, or give a glimpse of your systems in action. Many customers crave this “behind the scenes” look, Alton says.
But wait, there's more...
Besides boosting your brand, marketing videos attract more customers to your website, thanks to Google, says Swati Joshi in The Huffington Post.
"The fact that Google owns YouTube plays a role in video’s increased popularity," she says.
"Google has been constantly adjusting its algorithm to give its users a meaningful experience while searching. To satisfy user intent, they show a variety of results, and not just exact keyword matches. As a result, search results now prominently feature videos among top results."
Thursday, March 17, 2016
Micro Ads: Small is the New Big
Micro ads deliver macro results, according to a new study by IPG Media Lab.
When viewed on smartphones, micro ads—videos 5 to 15 seconds in length—yield better brand recall, preference and purchase intent than longer ads, the study found.
Micro ads also yield better results among Millennials than viewers of other ages.
Micro ads enjoy an advantage because they're bite-sized, the researchers say.
The ads enjoy an advantage when viewed on smartphones because they seem to dominate the tiny screens.
Millennials dig micro ads because they grew up with smartphones. They find micro ads more enjoyable and of higher quality than viewers of other ages.
The study also found micro ads work better when viewers are out and about, rather than home; and when the ads have voiceovers.
For a micro ad to drive more than just brand awareness, its minimum length should be 15 seconds, according to the study.
A micro ad shorter than that is simply too micro.
Thursday, March 10, 2016
Travel's Romance with Video
Travel brands will increasingly lean on video to seduce mobile-carrying customers, according to Skift.
As evidence, the newsletter cites the 25-minute reverie French Kiss, recently produced by Marriott.
"Instead of selling hotel rooms and airplane seats as commodities, brands are learning to tell stories using video that create an emotional connection with a specific audience," Skift says.
Leading the field, Marriott runs a full-scale, in-house studio that produces original shorts.
"Instead of selling hotel rooms and airplane seats as commodities, brands are learning to tell stories using video that create an emotional connection with a specific audience," Skift says.
Leading the field, Marriott runs a full-scale, in-house studio that produces original shorts.
Thursday, January 7, 2016
Why Monkey with Your Brand?
Mathematician Émile Borel said a century ago, if you provided an infinite number of monkeys typewriters, eventually they'd produce Hamlet.
Today he might say, if you provided them smartphones, eventually they'd produce The Godfather.
Despite having limited time and money, marketers seem convinced amateurs can produce broadcast-quality videos.
Why do they monkey with their brands?
In his blog, Prathap Suthan, chief creative officer at agency Bang In The Middle, warns marketers of their folly.
"There are billions of sadly made films finding their way into the great social sewer. They comprise all kinds of trash. Including films made by big brands which they conveniently call web films.
"Hello, your audience doesn’t realize the difference between a film made for the web versus television. For people, including all of us reading us, it’s a film. Most are badly made. Some are downright ugly. Very few are beautiful, and therefore shareable.
"Now the thing is, take your eyes off quality and finesse, and you have a sad film representing your company, product, or brand. A social film has to be equivalent to a regular TV film. It’s not just a web film anymore.
"Save yourself from the gutter and the clutter. Bad content is arsenic. It will eat your brand from inside."
Sunday, November 22, 2015
What Do Women Want?
What do female executives—or male ones, for that matter—want from B2B salespeople?
Personalized content.
Channeling Freud, Harris recently asked, When it comes to sales pitches, what do you want?
Harris learned executives want pitches that are personalized:
Personalized content.
Channeling Freud, Harris recently asked, When it comes to sales pitches, what do you want?
Harris learned executives want pitches that are personalized:
- 89% want pitches personalized to their company’s industry
- 83% want pitches personalized to their specific problem
- 70% want pitches personalized to their role in the company
The pollsters learned executives want sales emails with content:
- 84% want case studies
- 81% want articles
- 78% want white papers
- 72% want brochures
- 72% want videos
NOTE: Today's post is yet another milestone for Copy Points: No. 500. Coming soon: Post No. 501.
Tuesday, November 17, 2015
Government Communicators: Turn Citizens into Fans
Award-winning video producer Ann Ramsey contributed today's post. She is a senior producer at the US Department of Health & Human Services in Washington, DC.
Learn from peers. Organizations such as Federal Communicators Network, the National Association of Government Communicators, and the National Press Club will help you plan video strategies. Scanning the YouTube channels of agencies with goals similar to yours will also help. Government channels are listed in the GSA Social Media Registry.
Look around you. Government communicators can develop video content by cultivating in-house officials who come across well on camera (often, presence is better than pedigree). If an agency hosts an important forum, it’s a good idea to videotape it and amplify the link. At almost any event, an area can be set up for interviewing participants. If videotaping isn’t possible, audio-taping and photography are good alternatives.
Use inside help. Government communicators are smart to consider in-house video production, before hiring a PR firm. Many government departments already have TV studios with plenty of capacity. If your agency doesn't have one, take a look at sister agencies. In-house producers can save taxpayers' money.
Channel your videos. YouTube goes out of its way to help government agencies. For example, if asked, YouTube won't run ads on their channels. Government communicators should get in touch with Google to learn more.
Tailor the length. Video content on FaceBook and Twitter needs to be "snackable"—10-20 seconds long. Longer content belongs on dedicated video platforms, such as YouTube or iTunes.
Stay current. Keeping abreast of production trends helps government communicators create successful videos. Hot video trends are motion graphics, film-like shooting styles, and true-to-life testimonials. Audio and video podcasting are also surging in popularity.
Do it right. It behooves government communicators to preserve standards of quality and integrity on social media. When inviting public response, introduce only substantive topics, rather than “name this dog” sorts of trivia.
Mind the store. Comments, shares, and average length-per-view will give you an idea of audience engagement and are useful to track. Curating incoming comments allows urgent questions to be re-directed, and inappropriate comments to be deleted. Dated video material is best removed and archived.
Get found. The public turns to government for many urgent matters. Bizarre hashtags or “click-bait” naming strategies only stand in its way. Many highly viewed government YouTube videos sport transparent titles, such as “What are the Symptoms of the Flu?” Clear tags and titles take full advantage of how the public actually uses search engines.
Reach your viewers. YouTube’s built-in analytics reveal viewer demographics you can use to guide future outreach. Viewers should always be encouraged to subscribe to an agency’s channel, so new content will reach them. Stakeholders and partners can help you amplify a message to specific audiences.
Let it grow. Steady addition of new video episodes builds viewership. It often takes variations on a theme before results emerge. Experimenting with different versions, styles and platforms is well worthwhile.
Government communicators spend their time educating citizens about what their departments do.
Video, distributed through broadcast media and public-facing government Web sites, has long played a starring role in those efforts.
But citizens today, as they consume video at unprecedented rates, expect it to be served on social media platforms such as YouTube, FaceBook and Twitter.
Video, distributed through broadcast media and public-facing government Web sites, has long played a starring role in those efforts.
But citizens today, as they consume video at unprecedented rates, expect it to be served on social media platforms such as YouTube, FaceBook and Twitter.
With forethought and creativity, government communicators can use video to join the social media conversation—without breaking the bank or running roughshod over internal guidelines. Here's how:
Learn from peers. Organizations such as Federal Communicators Network, the National Association of Government Communicators, and the National Press Club will help you plan video strategies. Scanning the YouTube channels of agencies with goals similar to yours will also help. Government channels are listed in the GSA Social Media Registry.
Look around you. Government communicators can develop video content by cultivating in-house officials who come across well on camera (often, presence is better than pedigree). If an agency hosts an important forum, it’s a good idea to videotape it and amplify the link. At almost any event, an area can be set up for interviewing participants. If videotaping isn’t possible, audio-taping and photography are good alternatives.
Use inside help. Government communicators are smart to consider in-house video production, before hiring a PR firm. Many government departments already have TV studios with plenty of capacity. If your agency doesn't have one, take a look at sister agencies. In-house producers can save taxpayers' money.
Channel your videos. YouTube goes out of its way to help government agencies. For example, if asked, YouTube won't run ads on their channels. Government communicators should get in touch with Google to learn more.
Tailor the length. Video content on FaceBook and Twitter needs to be "snackable"—10-20 seconds long. Longer content belongs on dedicated video platforms, such as YouTube or iTunes.
Stay current. Keeping abreast of production trends helps government communicators create successful videos. Hot video trends are motion graphics, film-like shooting styles, and true-to-life testimonials. Audio and video podcasting are also surging in popularity.
Do it right. It behooves government communicators to preserve standards of quality and integrity on social media. When inviting public response, introduce only substantive topics, rather than “name this dog” sorts of trivia.
Mind the store. Comments, shares, and average length-per-view will give you an idea of audience engagement and are useful to track. Curating incoming comments allows urgent questions to be re-directed, and inappropriate comments to be deleted. Dated video material is best removed and archived.
Get found. The public turns to government for many urgent matters. Bizarre hashtags or “click-bait” naming strategies only stand in its way. Many highly viewed government YouTube videos sport transparent titles, such as “What are the Symptoms of the Flu?” Clear tags and titles take full advantage of how the public actually uses search engines.
Reach your viewers. YouTube’s built-in analytics reveal viewer demographics you can use to guide future outreach. Viewers should always be encouraged to subscribe to an agency’s channel, so new content will reach them. Stakeholders and partners can help you amplify a message to specific audiences.
Let it grow. Steady addition of new video episodes builds viewership. It often takes variations on a theme before results emerge. Experimenting with different versions, styles and platforms is well worthwhile.
Sunday, May 24, 2015
When Life Gives You Lemons
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Powered by Blogger.
2 MILLION READERS CAN'T ALL BE WRONG. Subscribe to Goodly now.
About my opinions
Oscar Wilde said it best: "In all matters of opinion, our adversaries are insane."
Search Goodly
















